Porter’s Five Forces: Understanding Market Competition
Business analysts don’t often evaluate the competition in the current industry. After all, how frequently do you work on a new product or company? But when you do, it’s important to start the project with an understanding of how industries compete. Porter’s Five Forces can assist you with this.
An industry’s competitive pressures can be examined using this straightforward yet effective framework.
What does Porter’s Five Forces actually mean, though? How is it used to evaluate a market’s level of competition? And how may AI be used to streamline this process?
Let’s start with the fundamentals and explore it.
What are Porter’s Five Forces?
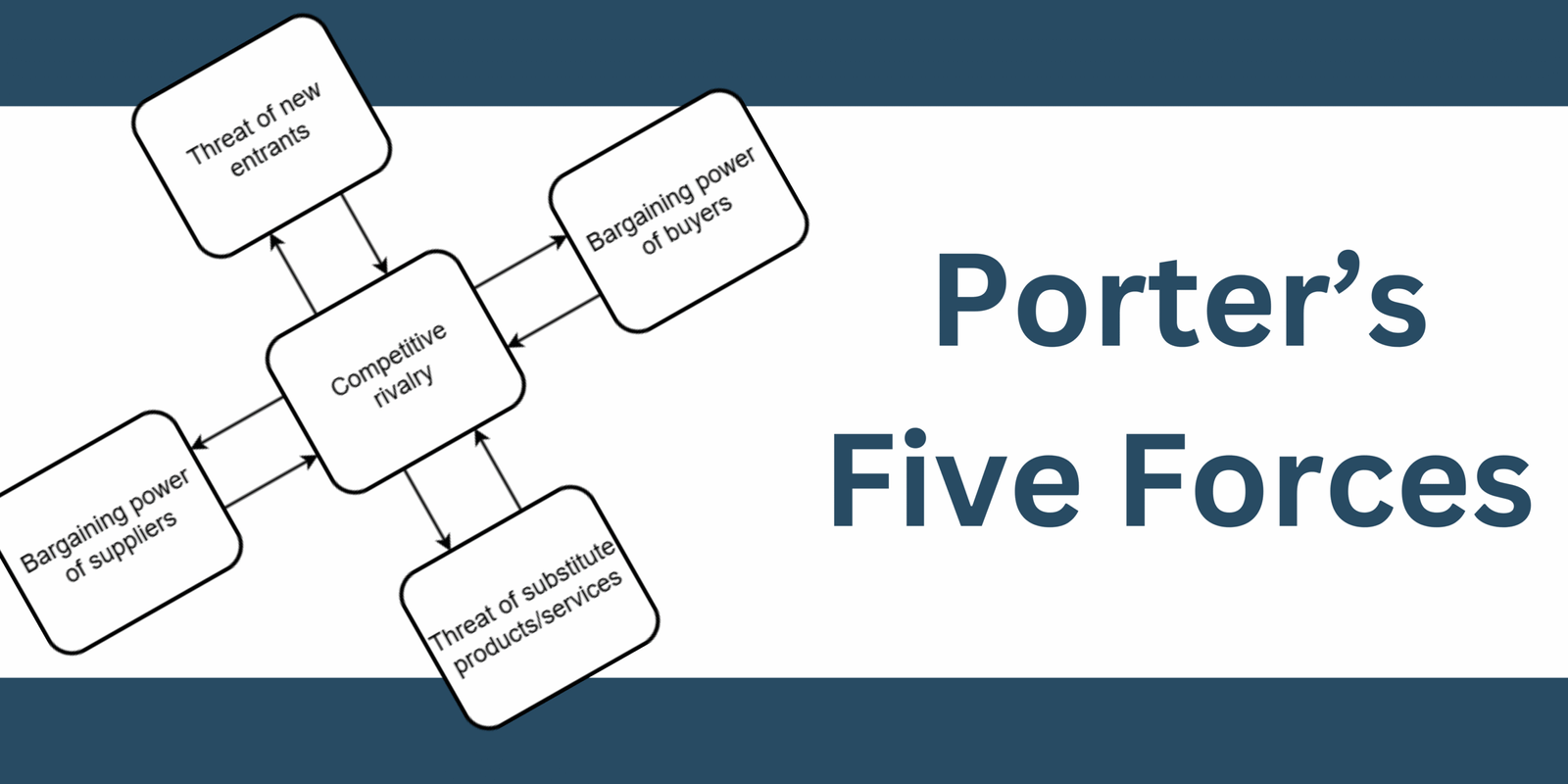
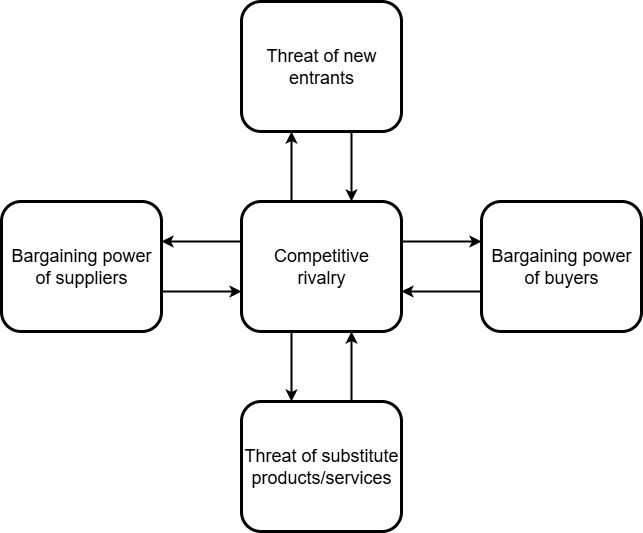
Porter’s Five Forces framework was introduced by Michael E. Porter in his 1979 book ‘Competitive Strategy’. It’s designed to help businesses understand the competitive forces that shape every industry, helping them make strategic decisions about pricing, product development, and more. These five forces are:
- Competitive rivalry
- Threat of new entrants
- Bargaining power of suppliers
- Bargaining power of buyers
- Threat of substitute products or services
Each of these forces affects the overall level of competition and profitability within an industry. Let’s dive deeper into what each one means and how it works.
1. Competitive rivalry
Competitive rivalry looks at the intensity of competition between existing companies in an industry. High competition can lead to price wars, innovation pushes, and even consolidation. In highly competitive industries, companies often focus on differentiation strategies to stand out from the pack.
The smartphone market is one of the most competitive industries today, with companies like Apple, Samsung, and Google constantly vying for market share. These companies compete on price, features, branding, and ecosystem integration. The intense rivalry forces companies to innovate frequently to retain consumer interest.
2. Threat of new entrants
The threat of new entrants refers to how easily new competitors can enter an industry and disrupt existing businesses. This force is particularly important for industries where barriers to entry are low. Think startups in tech or online retail.
Consider the fitness app industry. It has relatively low barriers to entry. Anyone with some coding skills and access to a smartphone app development platform can create an app. As a result, established players like Peloton face competition from new entrants constantly. These new competitors could potentially lower prices, offer innovative features, or attract users through creative marketing strategies.
3. Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers refers to the power suppliers have in influencing prices and terms within an industry. When there are few suppliers or when the supplier offers a unique product, their power increases.
Think about Apple and its suppliers. Apple’s reliance on specialized suppliers for unique hardware components, like chips for its iPhones, means those suppliers hold considerable power. If a supplier increases prices or experiences delays, Apple’s ability to produce and sell its products efficiently is impacted.
4. Bargaining power of buyers
The bargaining power of buyers refers to the power customers have to influence prices and terms. The more alternatives buyers have, or the more information they have, the more bargaining power they possess.
In the coffee shop industry, chains like Starbucks face pressure from buyers who can easily switch to other coffee chains or even local shops. However, Starbucks has managed to reduce the bargaining power of buyers by focusing on creating a unique customer experience with loyalty programs and a strong brand.
5. Threat of substitute products or services
Finally, the threat of substitutes refers to the likelihood that customers might switch to different products or services that meet the same need. The more substitutes available, the higher the pressure on companies to innovate and offer competitive prices.
In the transportation industry, the rise of Uber and other ride-sharing apps has posed a significant threat to traditional taxi services. Taxis, which once had a monopoly in many cities, now face competition from more affordable and convenient options, making it harder to charge premium fares.

When to conduct the analysis
Anytime you’re entering a new market, launching a product, or just trying to figure out why your competitors seem to be two steps ahead, conducting Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a smart move.
This tool helps you spot competitive pressures before they catch you off guard. It’s especially handy during strategic planning sessions, business case development, or when investors ask: “So… what’s stopping someone else from doing this?”
If you’re working in a rapidly changing industry or thinking about shifting your positioning, Five Forces can give you the outside-in view you didn’t know you needed.
Advantages and disadvantages of Porter’s Five Forces
The main advantage of this type of analysis is that it gives you a structured way to assess your competitive environment. Instead of guessing why sales are flat or why a new player is gaining traction, you get to break it down logically.
It’s simple, visual, and super helpful for spotting threats and understanding market dynamics. But it’s not perfect.
One downside? It focuses a lot on competition and not so much on internal strengths or external trends (you’ll want tools like SWOT or PESTLE for that). Plus, it’s a snapshot in time. It won’t capture fast-moving changes unless you revisit it regularly.
Still, as a starting point for strategic thinking, it’s one of the best tools out there.
How to use AI to generate Porter’s Five Forces analysis
After we’ve broken down the five forces and provided some practical examples, let’s examine how AI can facilitate this process.
By using AI tools like ChatGPT or specialized business strategy tools, you can generate detailed analyses for any industry. Here are a few ways to do this:
- Identify key data: Start by defining the industry or company you want to analyze.
- Input industry-specific details: Mention specifics about suppliers, buyers, market entry barriers, substitutes, and current competitors.
- Use AI-generated insights: Ask the AI to generate a detailed analysis of each force, based on the factors you’ve outlined.
AI tools can synthesize market trends, consumer behaviors, and competitor data to give you a comprehensive overview of the forces at play in any market.
Using the examples we mentioned above, here are a few ideas to structure your prompts.
AI prompt idea: Competitive rivalry
“Evaluate the level of industry rivalry in the smartphone market. Consider factors like market share distribution, competition in product features, and brand loyalty.”
This AI prompt would give you a quick snapshot of how competition plays out within the industry.
AI prompt idea: Threat of new entrants
“Analyze the threat of new entrants in the fitness app market using Porter’s Five Forces. Consider factors like development costs, market demand, and current competitors.”
This prompt could give you a well-rounded analysis of how new entrants might impact the fitness app market, and you could easily plug in this information into your own analysis.
AI prompt idea: Bargaining power of suppliers
“Evaluate the bargaining power of suppliers in the smartphone industry. Consider factors like the number of suppliers, their uniqueness, and how dependent companies are on them.”
By using this prompt, an AI tool like ChatGPT can help generate an analysis of the supplier landscape in any industry.
AI prompt idea: Bargaining power of buyers
“Analyze the bargaining power of buyers in the coffee shop industry. Include factors like brand loyalty, customer options, and price sensitivity.”
This prompt can provide insights into how buyer power shapes industries and what companies do to retain customer loyalty.
AI prompt idea: Threat of substitute products or services
“Assess the threat of substitutes in the transportation industry. Consider factors like the availability of alternatives, customer preferences, and price sensitivity.”
You can use this prompt to have an AI generate a detailed comparison of traditional vs. substitute services and how they impact market dynamics.
Conclusion
Porter’s Five Forces is a powerful framework that helps business analysts understand the competitive landscape of industries. By examining the five forces you can gain valuable insights into the competitive dynamics of any market.
And with the help of AI, you can speed up the process of creating these analyses, allowing you to make more data-driven and timely decisions about your business strategy.