PESTLE Analysis Made Simple: Including Examples and AI Tips
When it comes to understanding the external forces that could make or break your business strategy, PESTLE analysis is a go-to framework. It helps you zoom out and look at the world around you, because no business operates in a vacuum. If your strategy doesn’t account for politics, regulations, or even cultural shifts, you might be missing a big piece of the puzzle.
In this guide, we’ll break down what PESTLE analysis is, show you how to conduct one, and walk through real-life examples. Plus, you’ll get AI prompts to help you build your own PESTLE analysis faster.
What is PESTLE analysis?
By definition, PESTLE is a framework used to analyze the external macro-environmental factors that influence an organization’s performance and strategic decisions.
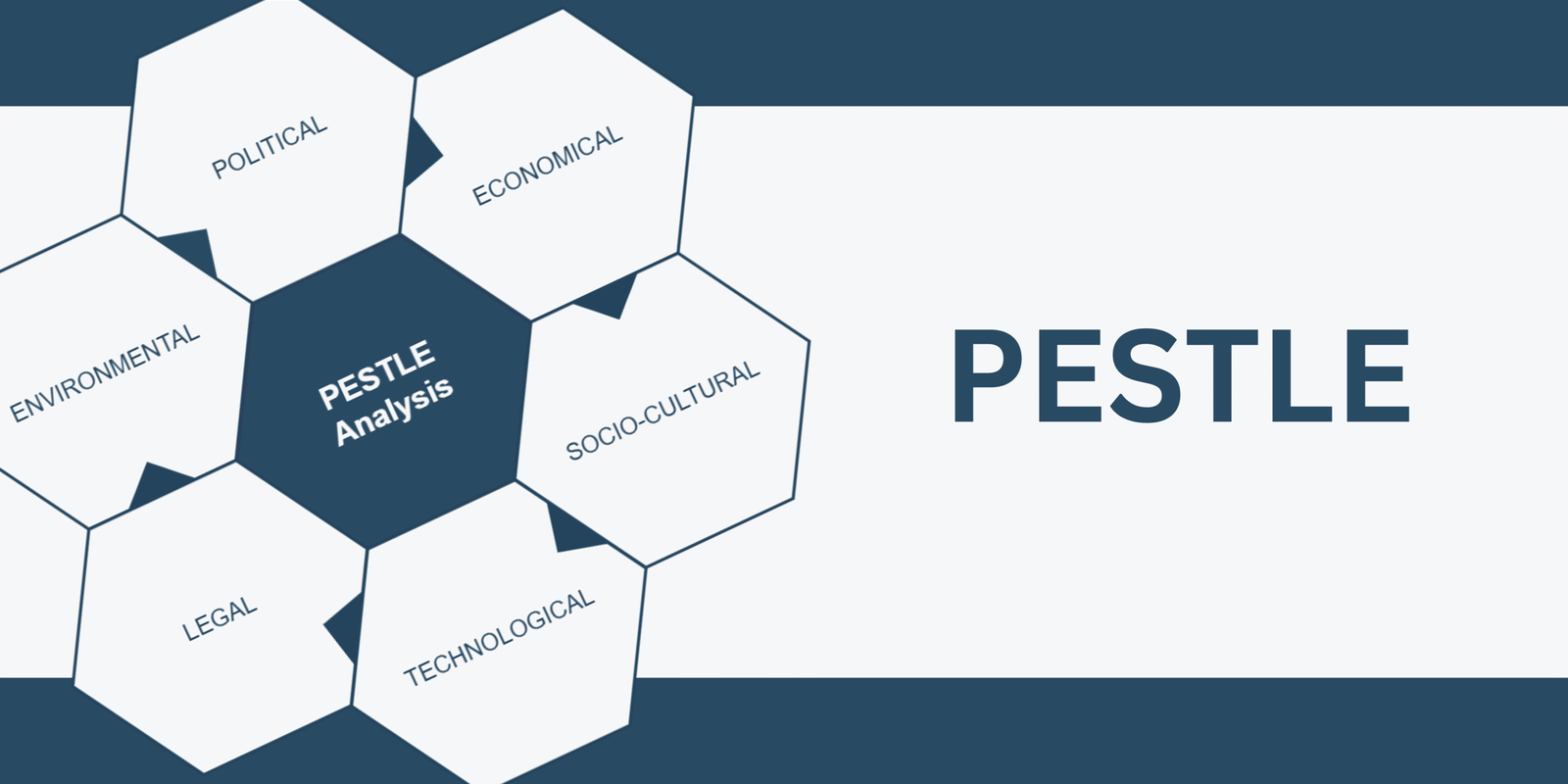
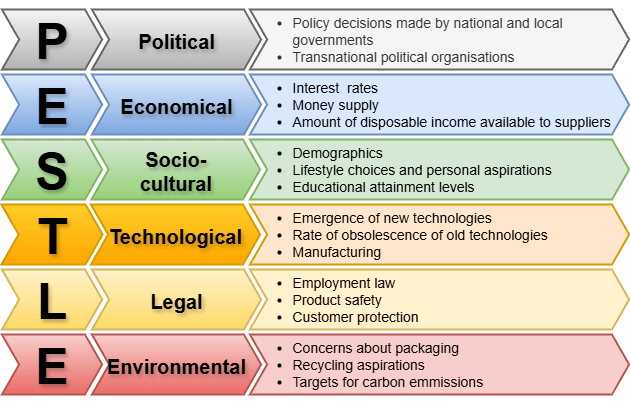
In simpler words, PESTLE analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate the external factors that can impact an organization. The acronym stands for:
- P – Political
- E – Economical
- S – Socio-cultural
- T – Technological
- L – Legal
- E – Environmental
It’s sometimes called PESTEL (same thing, different spelling). The goal? To identify the forces outside your control that could affect your strategy, operations, or market.
Why use a PESTLE analysis?
Think of it as a weather report for your business landscape. It doesn’t tell you what to do, but it helps you prepare for what’s coming. Here’s why it’s useful:
- Spot risks and opportunities early
- Adapt your strategy to external trends
- Understand the context behind customer behavior and market changes
- Support other analysis tools like SWOT or VMOST
PESTLE helps you answer the question: “What’s happening around us, and how might it affect what we’re trying to do?”
When to conduct a PESTLE analysis
You’ll want to run a PESTLE analysis in any of these situations:
- Launching a new product or market entry
- Conducting strategic planning
- Preparing a business case or market research
- Responding to industry disruption
- Planning for regulatory or environmental changes
It’s especially handy if you’re working in sectors affected by policy, tech evolution, or global trends like finance, education, healthcare, or energy.
PESTLE analysis step-by-step
Here’s a simple way to get started:
Political factors
These include international and local government policies, tax laws, trade restrictions, and political stability.
- Are there new regulations affecting our industry?
- How stable is the political climate in our markets?
Example: A change in EU data laws could impact how your tech product handles user information.
Economical factors
This includes inflation, interest rates, currency exchange, and overall economic health.
- Is the economy growing or slowing?
- Are customers tightening budgets?
- What is the amount of disposable income available to consumers?
Example: High inflation may lead consumers to cut non-essential spending, affecting luxury product sales.
Socio-cultural factors
Cultural trends, demographics, education levels, and lifestyle choices and personal aspirations fall here.
- What are the behaviour, preferences and attitude of you target customers?
- What social trends are influencing buyer behavior?
- Are our values still aligned with our audience?
Example: A growing demand for plant-based foods could create a new product opportunity in the food industry.
Technological factors
Think automation, AI, software innovations, and emerging platforms but also the rate or emergence and obsolescence of technologies.
- What new tech could disrupt our industry?
- Can we use tech to work smarter?
Example: Retailers using AI for personalized marketing are gaining an edge in customer retention.
Legal factors
Legal factors include employment and competition laws, copyright, consumer protections, product safety and compliance.
- Are there legal risks we haven’t accounted for?
- How are employment laws evolving?
Example: Remote work regulations in different countries could impact global hiring strategies.
Environmental factors
This includes sustainability, climate change, waste management, and resource scarcity.
- Are there environmental risks or regulations we should plan for?
- How can we be more eco-friendly?
- What are our targets for carbon emissions?
Example: Packaging legislation could force a rework of your product design.
Real-world PESTLE analysis examples
Let’s look at how PESTLE plays out in different industries.
| PESTLE Analysis Example: Electric Vehicle Market | |
| Factor | Example |
| Political | Government incentives for EV purchases |
| Economical | Rising fuel prices increase demand for alternatives |
| Socio-cultural | Growing eco-consciousness among Gen Z and Millennials |
| Technological | Advances in battery life and charging infrastructure |
| Legal | Emissions laws phasing out internal combustion engines |
| Environmental | Push for carbon neutrality and reduced urban air pollution |
| PESTLE Analysis Example: Online Education Industry | |
| Factor | Example |
| Political | National education funding and digital learning policies |
| Economical | Budget constraints in schools push adoption of cost-effective platforms |
| Socio-cultural | Students demanding flexible, on-demand learning |
| Technological | AI tutors, gamification, and mobile learning platforms |
| Legal | Privacy regulations for student data |
| Environmental | Reduced commuting aligns with sustainability goals |
AI prompts to help you generate a PESTLE analysis
Let AI tools like ChatGPT help you jumpstart your research and brainstorming. Try prompts like:
- “Create a PESTLE analysis for a fintech startup expanding into Asia.”
- “List political, economical, and legal risks for launching an eco-friendly clothing brand.”
- “Summarize PESTLE trends affecting higher education post-2025.”
- “Based on this industry [insert industry], generate a full PESTLE table with examples.”
These are great if you’re under time pressure or facilitating a team workshop.
Advantages and disadvantages of PESTLE analysis
Like every tool, PESTLE comes with pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Gives a broad view of external factors
- Great for early risk detection
- Helps align your strategy with the real world
- Pairs well with other tools (like SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces)
Disadvantages:
- Can become overly general or vague
- Needs to be updated regularly (external factors shift quickly)
- Doesn’t account for internal strengths or weaknesses
Combine PESTLE with other business analysis techniques
PESTLE works best when used alongside:
- SWOT Analysis. External factors from PESTLE feed right into the Opportunities/Threats sections.
- VMOST Analysis. PESTLE helps you align your mission and strategy with real-world trends.
- Porter’s Five Forces. Use both to cover internal competition and external macro shifts.
- Resource Audit. Once you spot external changes, check if your resources can handle them.
Final thoughts
PESTLE analysis might not predict the future, but it does help you prepare for it. From political shakeups to tech trends, understanding your macro-environment is crucial if you want to stay relevant and competitive.
So, the next time you’re planning a strategy, launching a new product, or just trying to understand market shifts, run a quick PESTLE. Better yet, pair it with AI prompts to fast-track the process and impress your stakeholders.